Viral Pharyngitis: Diagnosis And Treatment

Viral pharyngitis is the most common form of this disease: 60-80% of cases are caused by a virus. Despite this, people still use antibiotics in some countries, which is not a good habit. Namely, antibiotics are only effective against bacterial diseases.
Viral pharyngitis occurs more frequently in cold areas and during the cold seasons. It is a contagious infection, so the best way to prevent it is to avoid contact with an already infected person.
What is viral pharyngitis?
Viral pharyngitis is an inflammatory condition of the pharyngeal mucosa caused by a viral infection. The pharynx is a tubular anatomical structure that connects the oral cavity to the larynx and esophagus. It is located in the neck and is about 15 cm long in an adult.
The pharynx can become inflamed for a variety of reasons. Sometimes it is due to a bacterial infection or a fungus in the throat. In 30% of cases, no pathogen is found.
Viral pharyngitis is caused solely by the virus. The course of the disease depends on the type of virus involved and the treatment of the disease. Only in a few cases do sequelae occur.
What causes viral pharyngitis?
Viral pharyngitis is usually associated with a viral infection, that is, it is one of the symptoms of another infectious disease. When it occurs without another disease, it is referred to as nonspecific viral pharyngitis.
The disease usually starts gradually and in the latter case causes little harm. Normally, it heals on its own in two or three days. In other cases, viruses and related diseases are usually:
- Adenovirus, enterovirus, and rhinovirus all cause flu and pharyngitis.
- The influenza virus causes influenza and sometimes pharyngitis.
- The main disease may also be the herpes simplex virus (HSV).
- Epstein-Barr virus, a contagious virus that causes mononucleosis.
- HIV causes acute retroviral syndrome, usually associated with pharyngitis.
Identification of pharyngitis
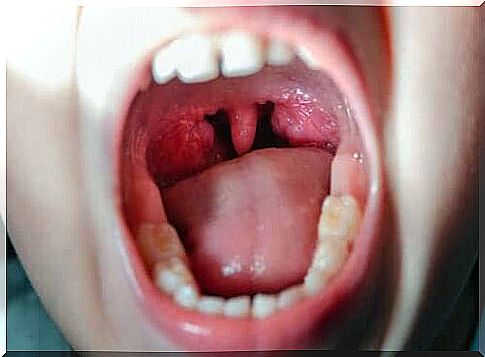
The type symptom of pharyngitis is a sore throat. In addition, there may be other symptoms of varying severity depending on the person. These are usually:
- Dry throat
- Pain when swallowing food or even plain saliva
- Tonsillitis
- Fever up to 38 degrees Celsius
- Headache
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
- Fatigue
Symptoms may vary depending on the type of virus that caused the disease. In acute viral pharyngitis, the pharynx is red and mucus-covered. In contrast, in chronic pharyngitis, the mucosa is pale, thin, and covered with thick mucus.
Diagnosis is made on the basis of symptoms by examining the patient and looking at his or her medical history. In some cases, your doctor will order a rapid test to detect streptococcal antigens to rule out bacterial pharyngitis.

How is viral pharyngitis treated?
There is no specific treatment for viral pharyngitis. Home remedies, such as gargling with warm salt water, often work. Thus, a small amount of salt is dissolved in a glass of warm water and gargled three times a day.
Drinking plenty of water also helps, as it cools the throat and helps the body get rid of viruses. In addition, it is best to rest adequately and avoid irritating substances such as tobacco and spicy, hard foods.
It is also important to avoid antibiotics when pharyngitis is caused by a virus. Antibiotics are of no use in this case, on the contrary: it strengthens the bacteria, making them resistant to those drugs.
Pharyngitis is rarely associated with sequelae. However, there are studies that pharyngotonsillitis has become more acute in recent years. This is one form of pharyngitis, which also affects the tonsils and is also caused by viruses in 80% of cases.