Health Effects Of Solar Radiation

The sun is the star closest to Earth and has often been the subject of dreaming, poetry, and numerous scientific studies. It is true that sunlight serves as a source of life and heat. However, solar radiation does not always promote good health.
The energy created by the sun spreads in the form of radiation, but not all of the radiation reaches Earth. The atmosphere absorbs much of it. However, radiation reaching the earth’s surface is the cause of many diseases such as heat stroke and skin cancer.
What kind of solar radiation is there?
There are many types of solar radiation. However, only two types of radiation are responsible for most health problems.
- Infrared radiation has low energy output and little force to penetrate the skin. So it is usually not responsible for skin problems. It warms the body and stimulates blood circulation. It also promotes thermoregulation and is responsible for sweating.
- Ultraviolet (UV) radiation doesn’t get much to Earth, but it can easily penetrate the inner layers of the skin. Depending on the skin type, UV radiation can cause tanning or more severe skin damage.

Impact of solar radiation on human health
Exposure to the sun promotes the synthesis of vitamin D, but it can also negatively affect human health if the exposure is excessive. The World Health Organization has warned of the harmful effects of solar radiation.
The WHO has also shown the following side effects:
- Increased risk of skin cancer.
- Sunburn skin burns of varying degrees.
- Premature and accelerated aging because solar radiation can promote the formation of free radicals and cause irreversible damage to the body’s molecules as well as cellular structures.
- Several eye diseases, including cataracts.
Other possible side effects caused by solar radiation are related to the inefficiency of the immune system. These include:
- Alteration of antigenic cell function. It is a group of cells in the immune system that affects the ability of the immune system to respond properly.
- Increased formation of cytokines, which stimulates or reduces the responsiveness of the immune system. These mediators reduce or multiply defense effectiveness according to the needs of the environment and infections caused by external factors.
- Changes in lymphocyte recirculation that may also affect the immune response. They change the way white cells spread in the tissues.
- Activation of T lymphocytes. These are the body’s defensive cells that protect people from infections and help fight cancer. They cause reactions that can lead to disease when improperly activated.
Effects of solar radiation on skin health
Skin cancer is one of the most significant health effects of solar radiation. Skin cancers have increased over the last 50 years and appear to be associated with gaps in the associated ozone layer. The function of this layer is to filter the sun’s rays.
Premature skin aging is another skin condition caused by excessive sun exposure. This effect of solar radiation is manifested through elastosis in the areas most exposed to the sun (face, neck and décolleté). They also lead to thickening of the skin, drying out and the formation of deep wrinkles.
Premature aging skin has spots and overpigmented areas due to a change in melanocytes. The skin becomes thick and rough, and the skin pores dilate. This is due to a phenomenon called hyperkeratinization.
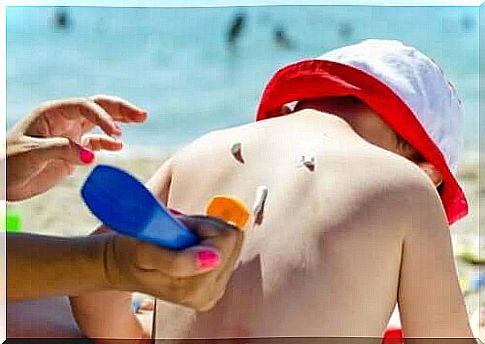
Prevention of damage caused by solar radiation
People react to the sun differently. Exposure to damage depends on skin type. That’s why it’s important to keep your own phototype in mind. For example, pale skin contains less melanin and thus is more sensitive to radiation than darker skin, while the latter is more prone to overpigmentation.
How can you prevent sun damage from occurring? It is important to note that such damage is cumulative. It means that a person is born with a certain sun tolerance and should not be exceeded during life. It is recommended to use sunscreen products that are suitable for your skin type.
Children under the age of three should not be in the sun for long periods of time. Take into account the recommended times, geographical location and season. Please also keep in mind that the intensity of solar radiation varies depending on altitude and season.
I hope you enjoyed this article.